Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing medical imaging, blending cutting-edge technology with healthcare to enhance diagnostics and treatment. This integration extends beyond simple image enhancements, promising faster, more precise diagnosis and personalized care. The exponential growth of AI in radiology and medical imaging, reflected in the 29.8% annual growth rate of related publications, underscores its increasing significance.
AI’s Potential in Medical Imaging
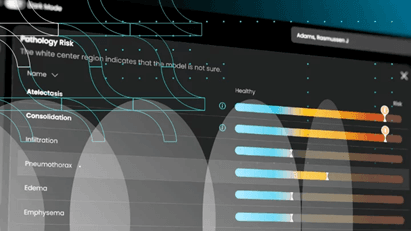
AI’s role in medical imaging is multifaceted, encompassing image quality enhancement, speed, early disease detection, and personalized medicine. Algorithms trained to identify subtle patterns enable AI to enhance image clarity, making conditions like fractures more detectable. Additionally, AI processes large datasets rapidly, reducing diagnostic bottlenecks and supporting faster patient care.
Incorporating deep learning, AI can identify disease-specific patterns, aiding early diagnosis. For instance, partnerships like that of Roche, Ibex Medical Analytics, and Amazon Web Services show how AI improves pathology workflows for cancer diagnosis, emphasizing efficiency and accuracy.
AI also aligns with personalized medicine, analysing imaging data alongside medical history to support tailored treatment plans, crucial for managing chronic conditions.
Current Applications
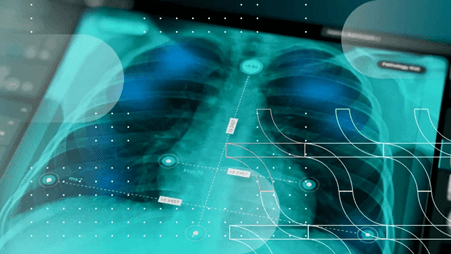
AI’s impact is evident in radiology, oncology, and neurology. Radiologists leverage AI to spot abnormalities in CT and MRI scans, such as pulmonary nodules, which may be missed by human analysis. In oncology, AI aids in breast cancer screenings, using deep learning to distinguish between benign and malignant growths with impressive accuracy.
AI’s role in neurology includes detecting strokes and identifying brain tissue changes linked to conditions like Alzheimer’s. For example, AI applied in diffusion-weighted MRI has shown top-tier performance, with significant accuracy in large clinical evaluations. These advancements bolster diagnostic practices, offering new avenues in personalized treatment and early intervention.
Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency

AI’s integration into imaging analysis has enhanced diagnostic accuracy and reduced human error. By processing extensive datasets, AI algorithms now match or surpass human radiologists in detecting diseases like pneumonia on chest X-rays. This is crucial for early treatment, significantly influencing patient outcomes.
AI also brings consistency, reducing variability caused by human fatigue or subjective judgment. It has proven effective in breast cancer screenings, where AI systems improve diagnostic reliability by minimizing errors.
Early disease detection is another area where AI excels. For instance, it can detect diabetic retinopathy in retinal images before symptoms appear, preventing blindness through timely intervention. By enhancing accuracy and enabling earlier diagnoses, AI elevates patient care and advances precision medicine.
Advancements and Challenges
AI’s role in medical imaging has been bolstered by advancements in machine learning algorithms and hardware like high-performance GPUs, enabling real-time image analysis. Post-2020, innovations in deep learning have paved the way for AI models that offer not only diagnostic precision but also interpretative insights into complex medical issues.
However, the path to AI integration is not without obstacles. Data privacy remains a major concern, as vast datasets are required for training AI models. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe is crucial to safeguard patient information. Additionally, implementing AI solutions can be costly, particularly for smaller medical practices. Addressing these challenges may involve partnerships with healthcare IT providers for gradual, cost-effective integration.
Healthcare professionals also require training to effectively use AI tools and incorporate AI-generated insights into their workflow. Building trust in AI through transparent communication and validation of its accuracy can mitigate resistance from practitioners wary of being replaced by technology.
Regulatory Landscape
AI in medical imaging involves navigating a complex regulatory framework. The U.S. FDA has set guidelines to ensure the safety and efficacy of AI-based tools, while Europe’s AI Act, introduced in 2024, mandates a transparent, human-centric approach. Adherence to data protection laws like HIPAA and GDPR is essential for maintaining patient trust and compliance.
The regulatory environment is evolving to accommodate rapid AI advancements. Balanced policies that encourage innovation while ensuring patient safety and privacy are necessary for sustainable AI integration in healthcare.
AI and Traditional Imaging Techniques
AI enhances traditional imaging methods like CT and MRI, offering faster image reconstruction and increased diagnostic accuracy. For example, AI can accelerate MRI scan times, improving patient throughput without compromising image quality. This synergy between AI and established modalities boosts radiologists’ capabilities, leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.
AI integration with ultrasound techniques has also improved cancer detection rates, showcasing the potential of combined AI-traditional imaging approaches.
Conclusion
AI in medical imaging represents more than a technological upgrade; it’s a shift reshaping diagnostics and treatment planning. By enhancing speed, accuracy, and personalization, AI contributes to an efficient, reliable healthcare system. While challenges remain, the future of AI in medical imaging is promising, marked by its potential for early disease detection, reduced diagnostic errors, and personalized treatment. As the technology matures, its integration is set to redefine patient care, driving forward the future of medical imaging.